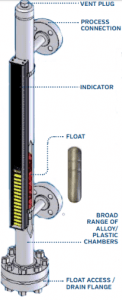
Dos and Don’ts of Sight Glass Selection for Improved Safety and Performance
Posted by Scott KloetzerAre you looking for better insight into your processes? Or to prevent waste? Improve safety? Enhance product quality? A sight glass observation port can check all these boxes and more. However, there are boxes equally as important to check off to select the right sight-glass window for your tanks and process vessels.
While the sight-glass port might be considered a minor part of an overall facility plan or design scheme, these highly engineered components play a critical role in enabling real-time monitoring of complex processes, enhancing safety and optimizing production performance. Following a list of dos and don’ts during selection can help ensure your choice provides clarity and durability.
Do take these five steps at a minimum before sight glass selection
-
Focus on process requirements
Before choosing the equipment, have a thorough understanding of the unique requirements of your industrial process. This includes factors such as fluid properties, operating conditions, and any potential or anticipated changes or variations that might occur over time. A deep understanding of the process ensures that the selected equipment will have proper performance, durability and reliability.
-
Evaluate temperature and pressure ratings
In addition to understanding the overall process requirements, know the pressure and temperature ratings required for the sight-glass observation equipment. Ensure the chosen equipment can safely withstand the maximum pressure and temperature expected during regular operation. Accounting for potential fluctuations and variations is critical for safety and equipment durability.
-
Consider the glass type
Different types of glass offer varying levels of resistance to chemical corrosion and thermal stress or are specified depending on the anticipated process temperature. Soda glass, a standard glass material, can be used when the temperatures are less than 300 °F.
Borosilicate glass is known for its excellent resistance to thermal shock, making it suitable for applications that have rapid temperature changes. Borosilicate glass is often preferred to soda glass even at lower temperatures due to its durability and is necessary when the temperatures rise above 300°F and up to 500°F.
METAGLAS®, a specialized type of glass, offers exceptional durability and resistance to aggressive chemicals, making it a preferred choice for highly corrosive applications. It can withstand high temperatures and has good optical clarity.
Quartz glass offers processors another option for high-temperature resistance.
As another specialty option, sapphire glass is a synthetic material known for its exceptional hardness and scratch resistance. On the Mohs scale, this substance ranks just below diamond, making it highly resistant to scratches and abrasion. It can be used when temperatures exceed 500°F.
Choosing the appropriate glass lends the observation port longevity and durability.
-
Prioritize Safety
Safety should be a primary concern when selecting sight-glass observation equipment. Ensure the chosen equipment meets the applicable safety standards and codes for your industry and location. Implement safety features (such as explosion-proof components) when necessary.
LJ Star offers explosion-proof components, along with its EX line of components, to assist with process observation. These components include lighting systems and cameras designed and tested for performance in more hazardous conditions. Always check the rating of any equipment designated for explosion-proof environments to ensure it is suitable for the processing environment and whether it is rated for gas or dust, for example.
-
Consider remote monitoring and cameras
Factors such as remote monitoring, process documentation, and worker safety could indicate the need to integrate a camera with the sight-glass observation equipment. A camera can be mounted on the window for real-time visibility, data recording and enhanced control. This contributes to both operational efficiencies and improves worker safety. Lights (and even wipers) can help provide a better view of the process by adding extra illumination or help clear obstructions.
Don’t neglect these considerations for process observation
-
Ignore potential process changes (or fail to consider process changes)
Don’t assume that the initial process conditions will remain constant. Industrial processes can evolve, leading to pressure, temperature or fluid composition changes. Failing to account for these variations in your equipment selection can result in operational issues or a need for frequent equipment replacement.
-
Choose equipment based solely on cost
Avoid selecting sight-glass observation equipment based solely on cost. Low-cost options might not offer the necessary durability or compatibility with your process. This can lead to increased maintenance time or expenses, unanticipated downtime and safety risks in the long run.
-
Overlook safety precautions
Never ignore safety regulations and standards for your specific industry and location. Non-compliance can lead to increased hazards, workplace incidents and potential legal consequences. Make sure the equipment is rated accordingly.
-
Neglect the mounting considerations
Will the sight glass be welded or bolted on the equipment? When welded into place, specify the hole size for the sight glass before making the vessel. If bolted on, remember that pressure limitations depend on the type of flange used. Follow DIN 28120 specification guidelines.
-
Forget about gasket compatibility
Always ensure the gasket material determined for use is compatible with the product it will come into contact with. Successful sight-glass performance rests on gasket integrity.
Selecting the right sight-glass observation equipment for industrial applications is a vital decision that directly impacts system integrity, safety and performance. By following these guidelines, engineering professionals and project managers can make informed choices that contribute to the long-term success of their processes and equipment.
Industrial applications are dynamic, and carefully considering factors like material compatibility, safety, and ongoing maintenance is essential for a successful installation. More information about selection criteria is found in our Step-by-Step Guide to Sight Glass Selection white paper. Or, contact our engineering team to discuss your planned project.